43 nitrogenous bases
Codon | Definition & Function | Britannica Codons are made up of any triplet combination of the four nitrogenous bases adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C), or uracil (U). Of the 64 possible codon sequences, 61 specify the 20 amino acids that make up proteins and three are stop signals. An example of a codon is the sequence AUG, which specifies the amino acid methionine. Nitrogenous Bases in DNA & RNA | What is a Nitrogen Base Pair? Apr 6, 2021 · A nitrogenous base is simply a molecule that contains nitrogen and has the chemical properties ...
Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA) Fact Sheet - Genome.gov Aug 24, 2020 · The four types of nitrogen bases found in nucleotides are: adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G) and cytosine (C). The order, or sequence, of these bases determines what biological instructions are contained in a strand of DNA. For example, the sequence ATCGTT might instruct for blue eyes, while ATCGCT might instruct for brown.
Nitrogenous bases
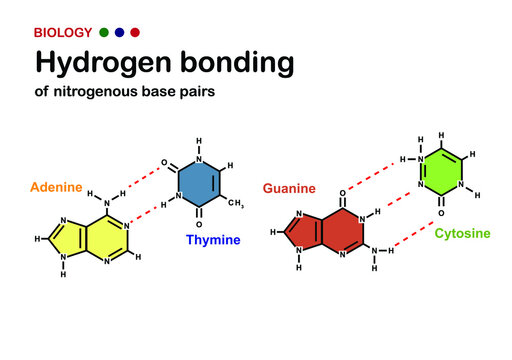
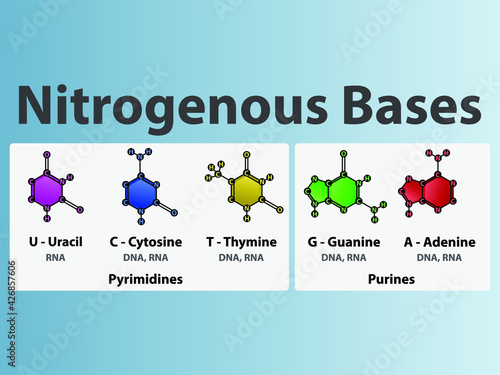
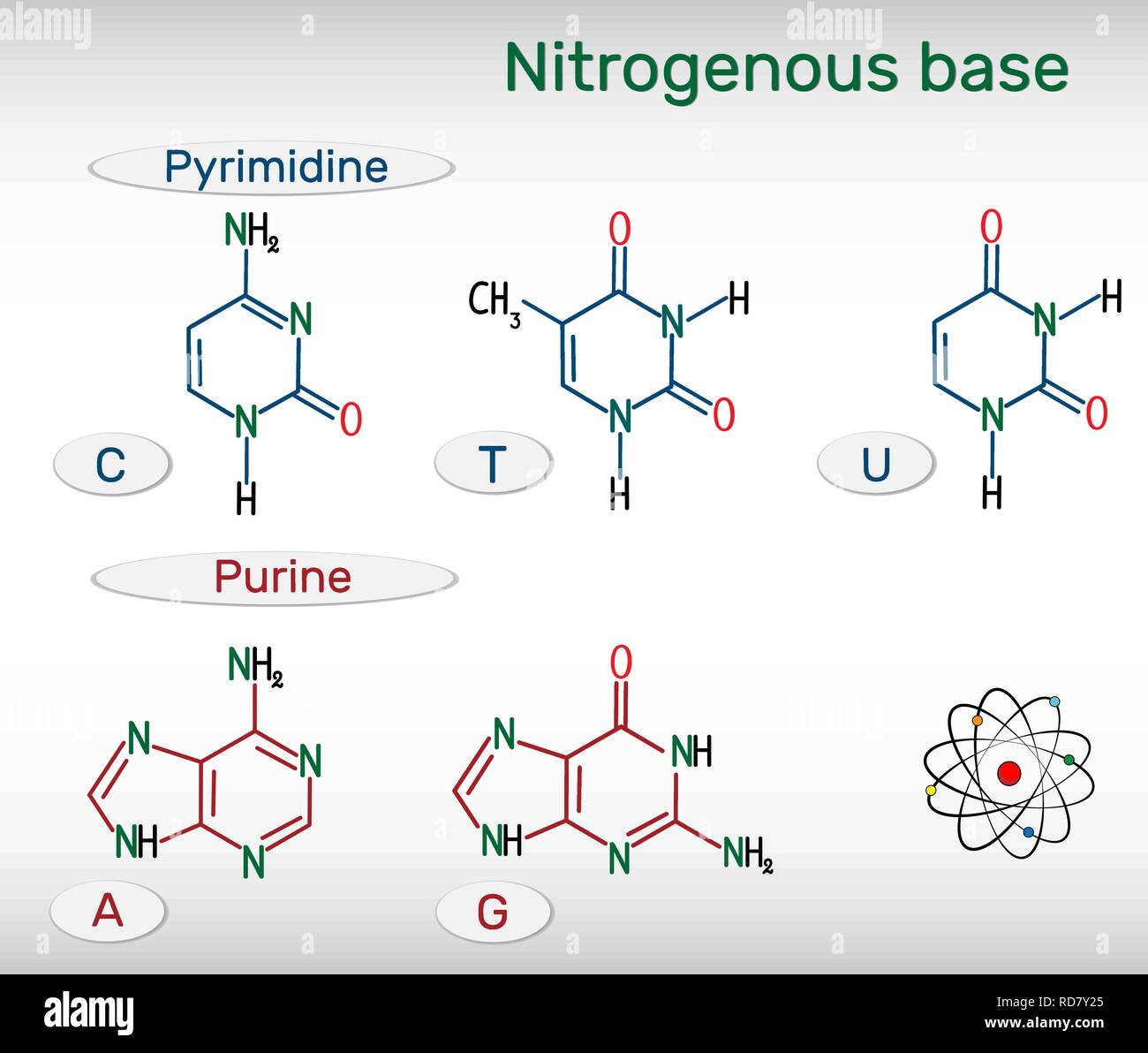
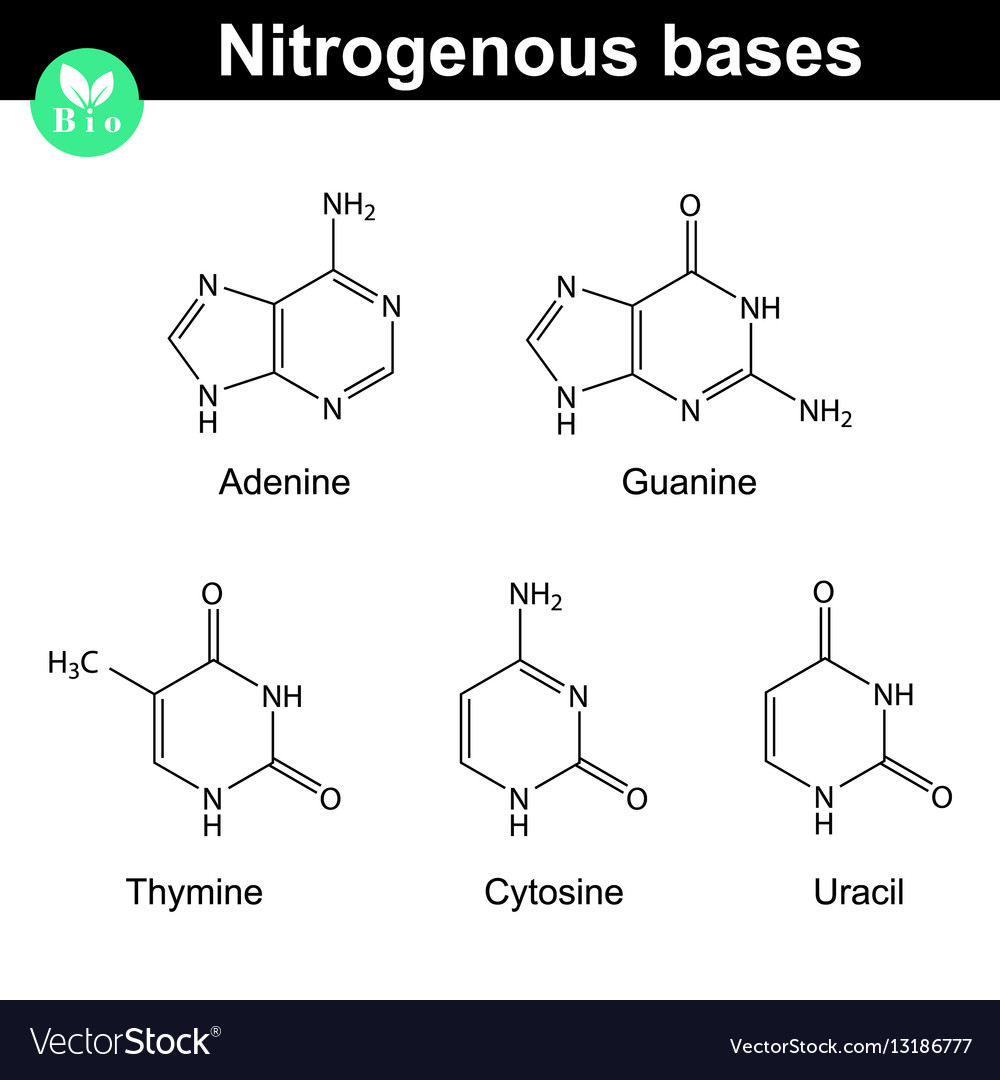
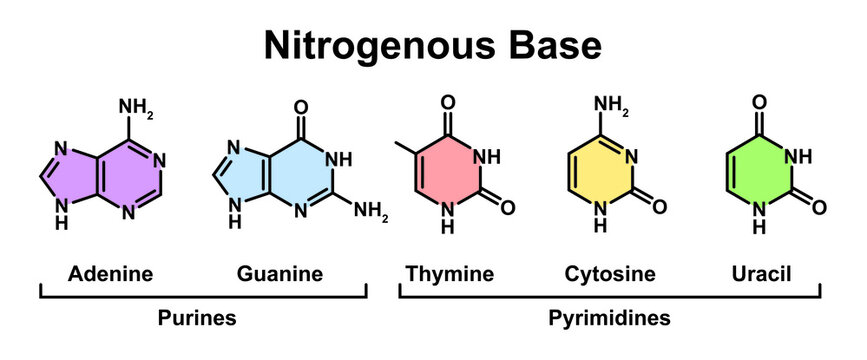
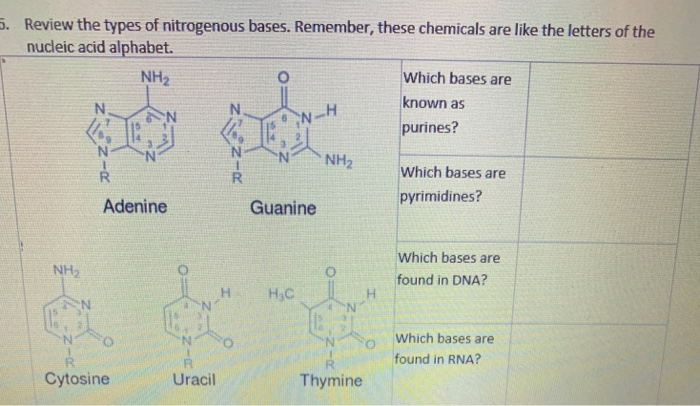
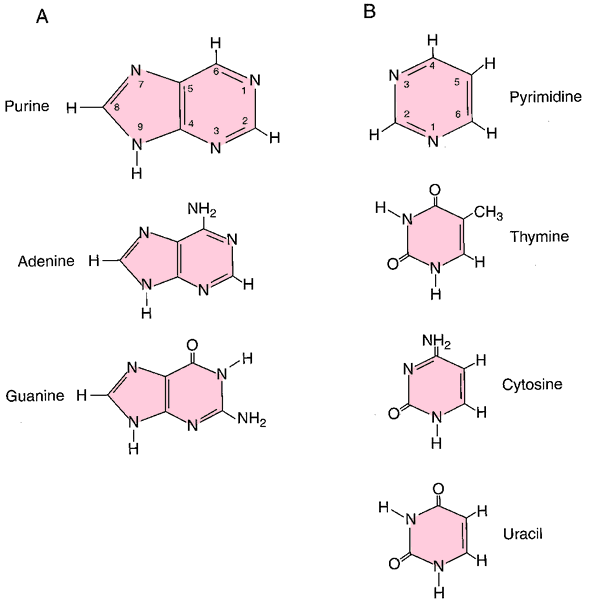
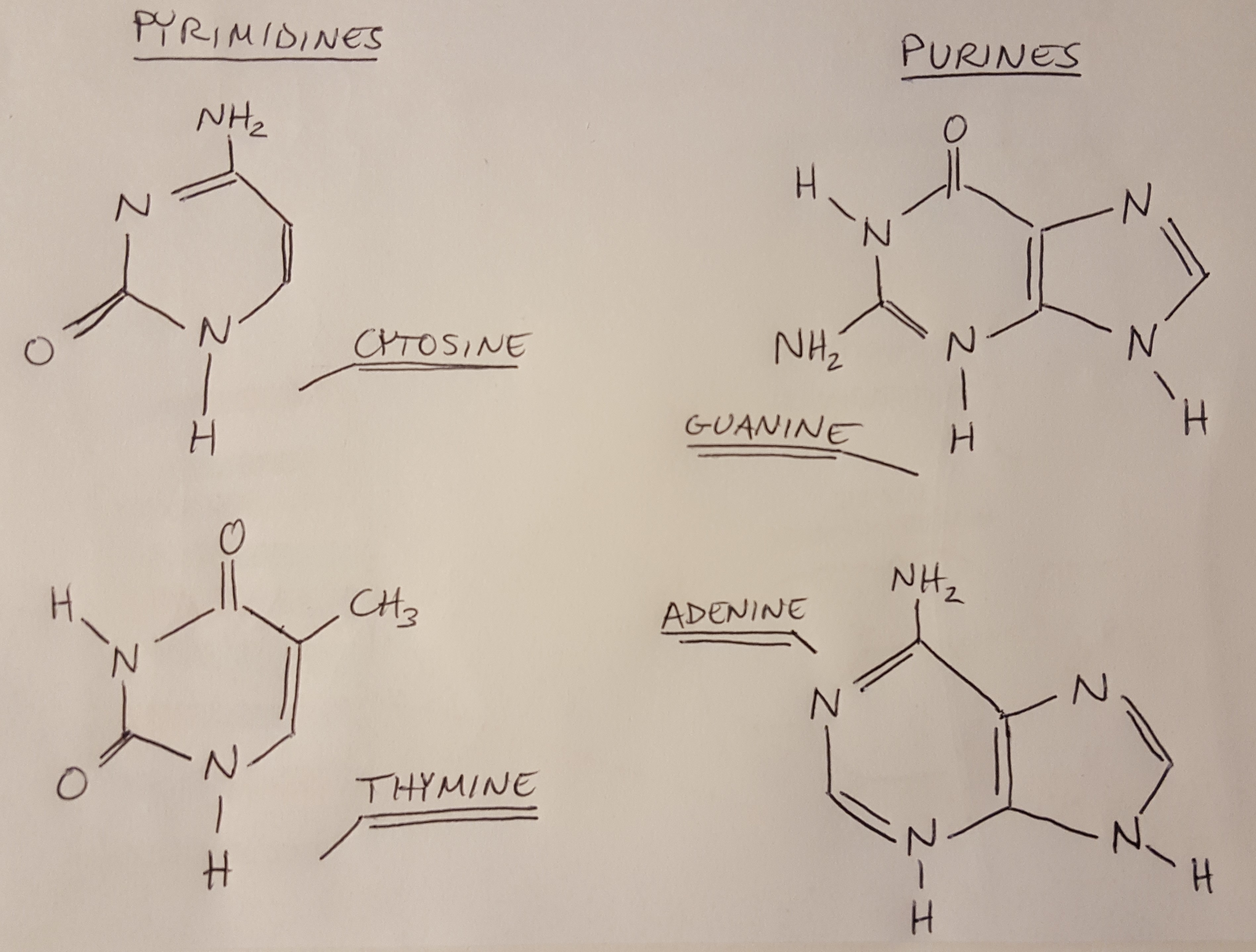
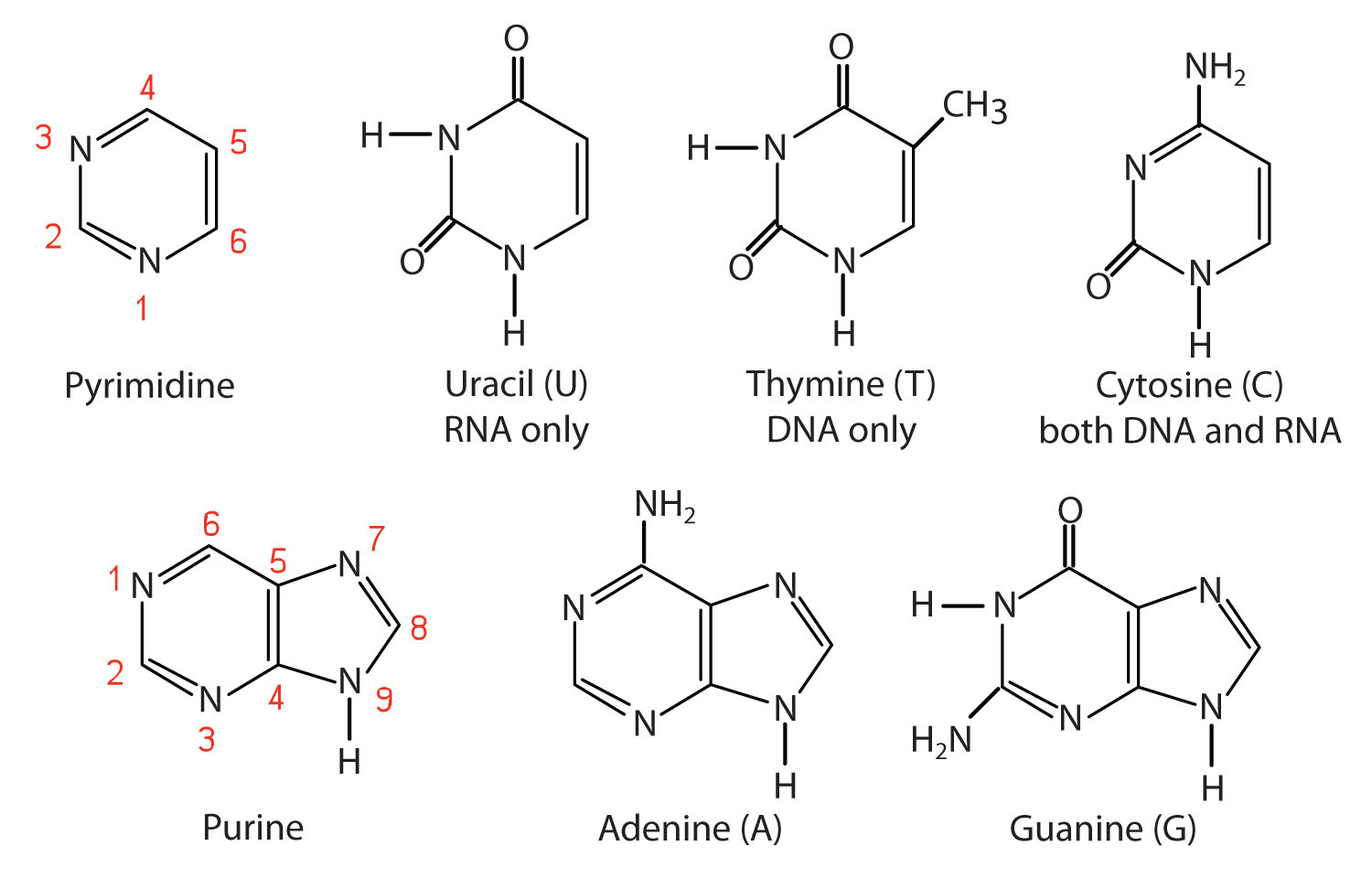
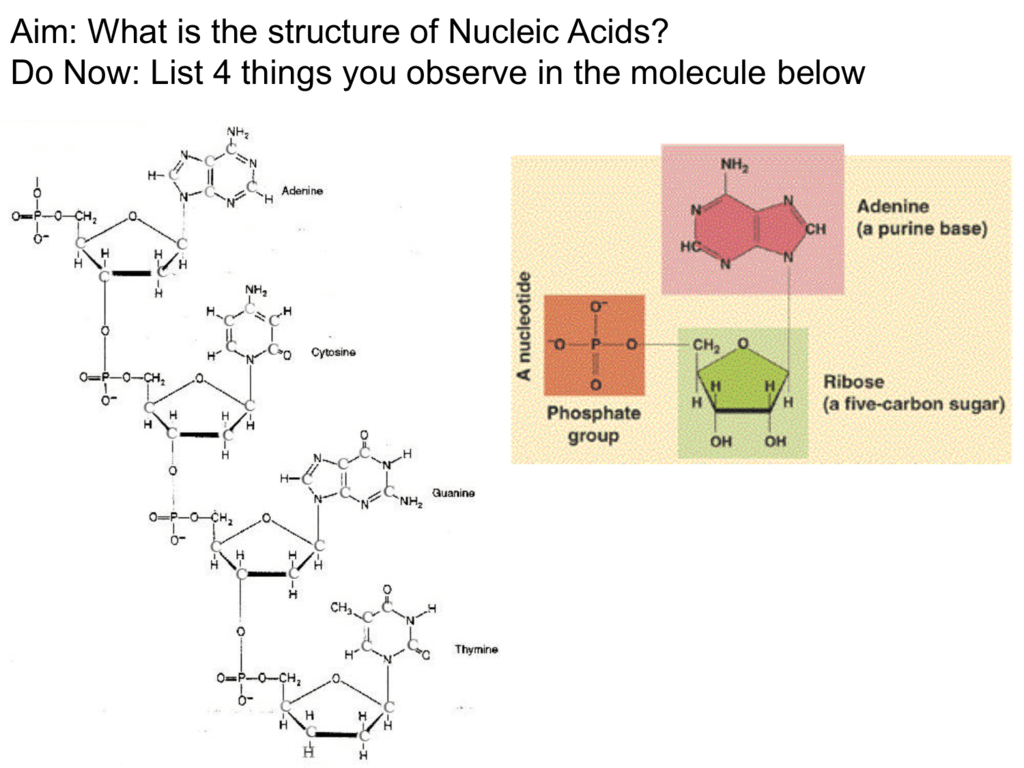
1.1: Nitrogenous bases, Nucleosides and Nucleotides The nitrogenous bases are purines such as adenine (A) and guanine (G), or pyrimidines such as cytosine (C), thymine (T), and uracil (U). Figure 1. Each nucleotide is made up of a sugar (ribose for nucleotides in RNA, deoxyribose for nucleotides in DNA), a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base. Nitrogenous Bases - GSU Nitrogenous Bases A set of five nitrogenous bases is used in the construction of nucleotides , which in turn build up the nucleic acids like DNA and RNA . These bases are crucially important because the sequencing of them in DNA and RNA is the way information is stored. RNA | Definition, Structure, Types, & Functions | Britannica The nitrogenous bases in RNA are adenine, guanine, cytosine, and uracil, which replaces thymine in DNA. The ribose sugar of RNA is a cyclical structure consisting of five carbons and one oxygen . The presence of a chemically reactive hydroxyl (−OH) group attached to the second carbon group in the ribose sugar molecule makes RNA prone to hydrolysis .
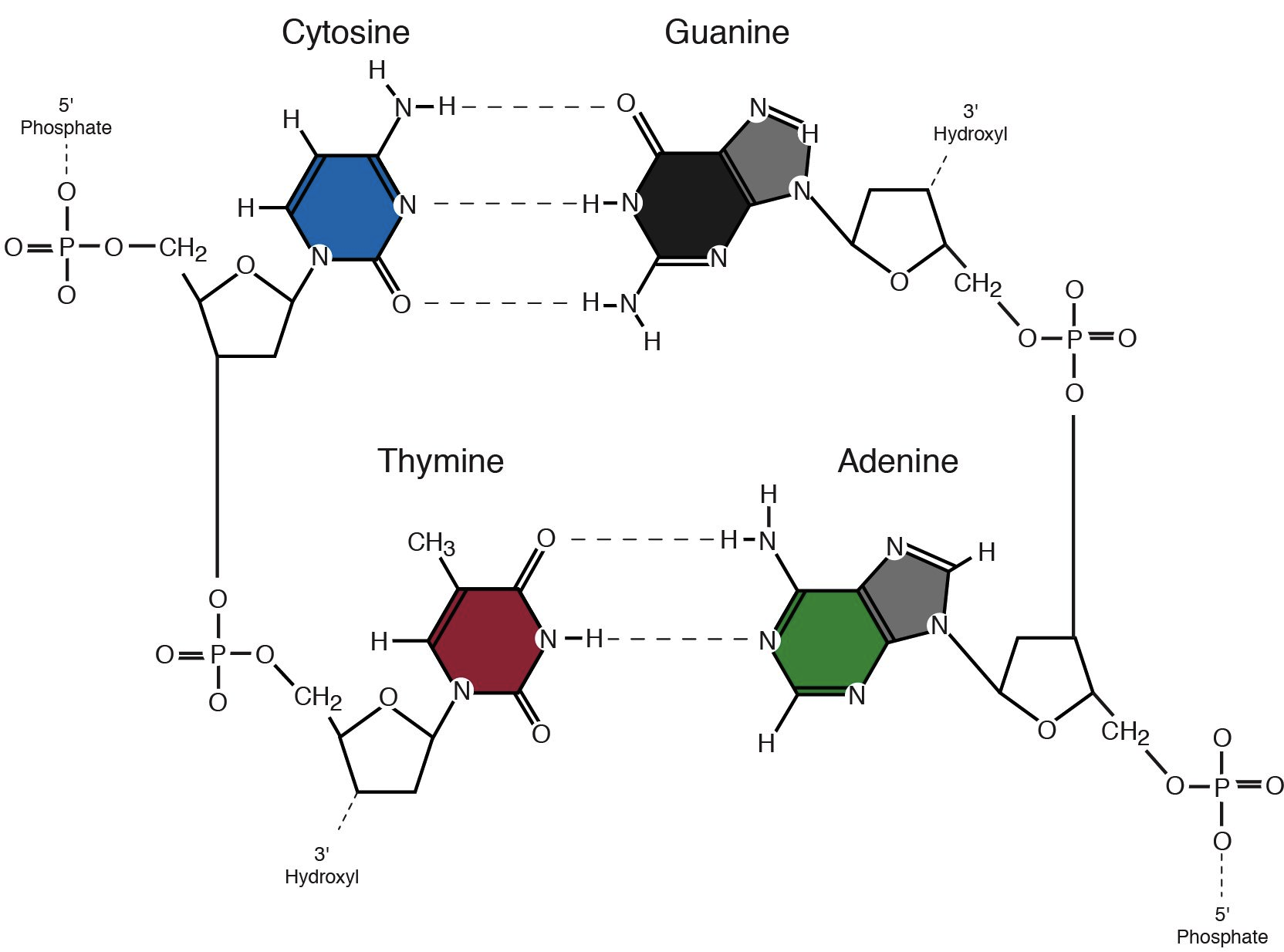
Nitrogenous bases. Nucleic acid - Wikipedia The nucleobases are joined to the sugars via an N-glycosidic linkage involving a nucleobase ring nitrogen (N-1 for pyrimidines and N-9 for purines) and the 1' carbon of the pentose sugar ring. Non-standard nucleosides are also found in both RNA and DNA and usually arise from modification of the standard nucleosides within the DNA molecule or the primary (initial) RNA transcript. RNA | Definition, Structure, Types, & Functions | Britannica The nitrogenous bases in RNA are adenine, guanine, cytosine, and uracil, which replaces thymine in DNA. The ribose sugar of RNA is a cyclical structure consisting of five carbons and one oxygen . The presence of a chemically reactive hydroxyl (−OH) group attached to the second carbon group in the ribose sugar molecule makes RNA prone to hydrolysis . Nitrogenous Bases - GSU Nitrogenous Bases A set of five nitrogenous bases is used in the construction of nucleotides , which in turn build up the nucleic acids like DNA and RNA . These bases are crucially important because the sequencing of them in DNA and RNA is the way information is stored. 1.1: Nitrogenous bases, Nucleosides and Nucleotides The nitrogenous bases are purines such as adenine (A) and guanine (G), or pyrimidines such as cytosine (C), thymine (T), and uracil (U). Figure 1. Each nucleotide is made up of a sugar (ribose for nucleotides in RNA, deoxyribose for nucleotides in DNA), a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base.











:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/molecular-model-of-cytosine-154932860-58693b9f3df78ce2c39e4f9c.jpg)














Komentar
Posting Komentar